Abstract
Mini Review
The Fundamental Role of Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Drinking Water, in the Etiopathogenesis, Prevention, Treatment and Recovery of Cerebral Vascular Events (Stroke)
Arturo Solís Herrera*
Published: 16 January, 2025 | Volume 9 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-006
Stroke is a clinically defined syndrome of acute focal neurological deficit attributed to vascular injury (infarction, hemorrhage) of the central nervous system. Stroke is the second leading cause of death and disability worldwide. Stroke is not a single disease but can be caused by a wide range of risk factors, disease processes and mechanisms. Approximately 15% of strokes worldwide are the result of intracerebral hemorrhage, which can be deep (basal ganglia, brainstem), cerebellar or lobar. A minority (about 20%) of intracerebral hemorrhages are caused by macrovascular lesions (vascular malformations, aneurysms, cavernomas), venous sinus thrombosis or rarer causes.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001064 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Blood vessels; Brain vasculature; CSF; Oxygen; Stroke; Vascular cerebral events; Water dissociation
References
- Kuriakose D, Xiao Z. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7609. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207609
- Kelly-Hayes M. Influence of age and health behaviors on stroke risk: Lessons from longitudinal studies. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:S325–S328. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02915.x
- Collaborators G.S. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:439–458. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30034-1
- Appelros P, Stegmayr B, Terént A. Sex differences in stroke epidemiology: A systematic review. Stroke. 2009;40:1082–1090. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.108.540781
- Chen JC. Geographic determinants of stroke mortality: Role of ambient air pollution. Stroke. 2010;41:839–841. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.110.578476
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Oct;20(10):795-820. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00252-0
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update. A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2009 Feb 23;121(7):948-54. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.192666
- Lanska DJ. Geographic distribution of stroke mortality in the United States: 1939–1941 to 1979–1981. Neurology. 1993;43:1839–1851. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.43.9.1839
- Lanska DJ, Kuller LH. The geography of stroke mortality in the United States and the concept of a stroke belt. Stroke. 1995;26:1145–1149. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.26.7.1145
- Lanska DJ, Kryscio R. The geographic distribution of hospital admissions, case fatality, and mortality from stroke among Medicare enrollees. Neurology. 1994;44:1541-1550. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.44.8.1541
- Nefzger MD, Kuller LH, Lilienfeld AM, Diamond EL, Miller GD, Stolley PD, et al. Three-area epidemiologic study of geographic differences in stroke mortality, I: Background and methods. Stroke. 1977;8:546-550. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.8.5.546
- Kovar MG, Pokras R, Collins JG. Trends in medical care and survival from stroke. Ann Epidemiol. 1993;3:466-470. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/1047-2797(93)90097-n
- Dyken ML, Wolf PA, Barnett HJ, Bergen JJ. Risk factors in stroke: A statement for physicians by the Subcommittee on Risk Factors and Stroke of the Stroke Council. Stroke. 1984;15:1105-1111.
- Lyon JL, Bishop CT, Nielsen NS. Cerebrovascular disease in Utah, 1968-1971. Stroke. 1981;12:564-566. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.12.5.564
- Takahashi E. On the geographic distribution of death rates from vascular lesions affecting the central nervous system in the United States: An epidemiological hypothesis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1962;76:224-232. Available from: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/tjem1920/76/3/76_3_224/_pdf
- Gover M. Statistical studies of heart disease, IV: Mortality from heart disease (all forms) related to geographic section and size of city. Public Health Rep. 1949;64:439-456. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18114617/
- Howard G, Evans GW, Pearce K, Howard VJ, Bell RA, Mayer EJ, et al. Is the stroke belt disappearing? An analysis of racial, temporal and age effects. Stroke. 1995;26:1153-1158. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.26.7.1153
- Wing S, Casper M, Davis WB, Pellom A, Riggan W, Tyroler HA. Stroke mortality maps: United States whites aged 35-74 years, 1962-1982. Stroke. 1988;19:1507-1513. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.19.12.1507
- Solís Herrera A, Arias Esparza MC. Oxygen from the atmosphere cannot pass through the lung tissues and reach the bloodstream. The unexpected capacity of the human body to dissociate the water molecule. J Pulmonol Res Rep. 2022;SRC/JPRR-133. Available from: https://doi.org/10.47363/JPRR/2022(4)124
- Herrera AS. The disdain importance of dissolved oxygen levels in drinking water in pandemic control. Adv Ecol Environ Res. 2020;5(11):296-299. Available from: https://www.ss-pub.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/AEER2020102201.pdf
- Blaszczak JR, Koenig LE, Mejia FH, Gómez-Gener L, Dutton CL, Carter AM, et al. Extent, patterns, and drivers of hypoxia in the world's streams and rivers. Limnol Oceanogr Lett. 2023;8:453-463. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/lol2.10297
- Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) For Dissolved Oxygen in Savannah Harbor Savannah River Basin Chatham and Effingham Counties, Georgia, Jasper County, South Carolina. Available from: https://epd.georgia.gov/sites/epd.georgia.gov/files/related_files/site_page/EPA_SavannahHarbor_DO_TMDL_2006.pdf
- Ji X, Shang X, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M. Prediction of dissolved oxygen concentration in hypoxic river systems using support vector machine: A case study of Wen-Rui Tang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017;24:16062–16076. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28537025/
- Ni X, Zhou F, Zeng D, Li D, Zhang T, Wang K, et al. Long-term observations of hypoxia off the Yangtze River Estuary: Toward prediction and operational application. In: Frontiers in Ocean Observing: Emerging Technologies for Understanding and Managing a Changing Ocean. E.S. Kappel, V. Cullen, M.J. Costello, L. Galgani, C. Gordó-Vilaseca, A. Govindarajan, S. Kouhi, C. Lavin, L. McCartin, J.D. Müller, B. Pirenne, T. Tanhua, Q. Zhao, S. Zhao, eds. Oceanography. 2023;36(Supplement 1):40–41. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2023.s1.13
- Blaszczak JR. Distribution, frequency, and global extent of hypoxia in rivers. U.S. Geological Survey. 2021.
- Pu L, Wang L, Zhang R, Zhao T, Jiang Y, Han L. Projected global trends in ischemic stroke incidence, deaths and disability-adjusted life years from 2020 to 2030. Stroke. 2023;54(5):1330-1339. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.040073
- Pope CA, Dockery DW. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2006;56:709–742. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2006.10464485
- Bell ML, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987–2000. JAMA. 2004;292:2372–2378. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.292.19.2372
- Hong YC, Lee JT, Kim H, Kwon HJ. Air pollution: A new risk factor in ischemic stroke mortality. Stroke. 2002;33:2165–2169. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000026865.52610.5b
- Wellenius GA, Schwartz J, Mittleman MA. Air pollution and hospital admissions for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke among Medicare beneficiaries. Stroke. 2005;36:2549–2553. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000189687.78760.47
- Dockery DW, Pope CA 3rd, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME, et al. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1753–1759. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199312093292401
- Simkhovich BZ, Kleinman MT, Kloner RA. Air pollution and cardiovascular injury: Epidemiology, toxicology, and mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:719–726. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2008.05.029
- Hutchins MG, Qu Y, Charlton MB. Successful modelling of river dissolved oxygen dynamics requires knowledge of stream channel environments. J Hydrol. 2021;603(B):126991. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126991
Figures:

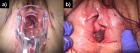
Figure 1
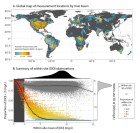
Figure 2
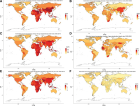
Figure 3
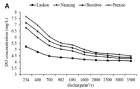
Figure 4
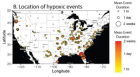
Figure 5
Similar Articles
-
Postural Stability Induced by Supervised Physical Training may improve also Oxygen Cost of Exercise and Walking Capacity in Post-Menopause, Obese WomenFernanda Velluzzi,Massimiliano Pau,Andrea Loviselli,Raffaele Milia,Daniela Lai,Daniele Concu,Gianmarco Angius,Abdallah Raweh,Andrea Fois,Alberto Concu*. Postural Stability Induced by Supervised Physical Training may improve also Oxygen Cost of Exercise and Walking Capacity in Post-Menopause, Obese Women. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001001; 1: 001-011
-
Influence of an integrated rehabilitative treatment on the modification of body representation in patients affected by Unilateral Spatial NeglectMaurizio Falso*,Michela Delpero,Eleonora Cattaneo. Influence of an integrated rehabilitative treatment on the modification of body representation in patients affected by Unilateral Spatial Neglect. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001023; 2: 087-100
-
Neuroanatomical profile of hemineglect in patient’s body image modificationMaurizio Falso*,Eleonora Cattaneo Psy. Neuroanatomical profile of hemineglect in patient’s body image modification. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001029; 4: 001-008
-
Efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation and over-ground walking task on functional mobility and quality of life of stroke survivorsCaleb A Adeagbo*,Caleb AO Gbiri,Olajide A Olawale. Efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation and over-ground walking task on functional mobility and quality of life of stroke survivors. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001037; 4: 049-056
-
Comparative efficacy of inspiratory, expiratory and combined respiratory muscle training on the pulmonary functions and chest expansion in acute stroke survivorsAdeogun Abiodun A*,Umar Dolapo K. Comparative efficacy of inspiratory, expiratory and combined respiratory muscle training on the pulmonary functions and chest expansion in acute stroke survivors. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001040; 5: 010-018
-
The Fundamental Role of Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Drinking Water, in the Etiopathogenesis, Prevention, Treatment and Recovery of Cerebral Vascular Events (Stroke)Arturo Solís Herrera*. The Fundamental Role of Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Drinking Water, in the Etiopathogenesis, Prevention, Treatment and Recovery of Cerebral Vascular Events (Stroke). . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001064; 9: 001-006
-
Insights into the Complexity of Paradoxical Antioxidants Behavior. And the Reasons for it’s almost Zero or no Effect on StrokeArturo Solís Herrera*,María del Carmen Arias Esparza,Sergey Suchkov. Insights into the Complexity of Paradoxical Antioxidants Behavior. And the Reasons for it’s almost Zero or no Effect on Stroke. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001065; 9: 007-012
-
The Inverse Relationship between Acute Myocardial Infarction and Dissolved Oxygen Levels in WaterArturo Solís Herrera*,María del Carmen Arias Esparza,Ruth Isabel Solís Arias. The Inverse Relationship between Acute Myocardial Infarction and Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Water. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001066; 9: 013-023
Recently Viewed
-
Cystoid Macular Oedema Secondary to Bimatoprost in a Patient with Primary Open Angle GlaucomaKonstantinos Kyratzoglou*,Katie Morton. Cystoid Macular Oedema Secondary to Bimatoprost in a Patient with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Int J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001059; 9: 001-003
-
Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of LiteratureNeha Singh,Gaurav Raj,Akshay Kumar,Deepak Kumar Singh,Shivansh Dixit,Kaustubh Gupta*. Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of Literature. J Radiol Oncol. 2025: doi: ; 9: 050-053
-
Depression as a civilization-deformed adaptation and defence mechanismBohdan Wasilewski*,Olha Yourtsenyuk,Eugene Egan. Depression as a civilization-deformed adaptation and defence mechanism. Insights Depress Anxiety. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001013; 4: 008-011
-
Drinking-water Quality Assessment in Selective Schools from the Mount LebanonWalaa Diab, Mona Farhat, Marwa Rammal, Chaden Moussa Haidar*, Ali Yaacoub, Alaa Hamzeh. Drinking-water Quality Assessment in Selective Schools from the Mount Lebanon. Ann Civil Environ Eng. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acee.1001061; 8: 018-024
-
Rapid Microbial Growth in Reusable Drinking Water BottlesQishan Liu*,Hongjun Liu. Rapid Microbial Growth in Reusable Drinking Water Bottles. Ann Civil Environ Eng. 2017: doi: 10.29328/journal.acee.1001007; 1: 055-062
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."