Abstract
Research Article
Effect of Lower Extremity Training in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Ann Reena Rajan*
Published: 12 February, 2024 | Volume 8 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-004
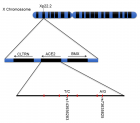
Background: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a symmetrical length-dependent sensorimotor polyneuropathy due to chronic hyperglycemia. The World Health Organization (WHO) identified diabetes as a major global health concern. Diabetic neuropathy is characterized by motor dysfunctions (weakness and atrophy) especially at the distal muscles of lower limbs, and impaired dynamic muscular control in type 2 diabetes patients. Symptoms start in a distal-to proximal pattern in the feet, and ankle and proximally in the hip and knee for both flexors and extensors. Proximal muscle weakness affects postural stability. Dorsiflexor weakness causes increased hip, knee flexion and metatarsophalangeal extension in the initial swing whereas weakness in plantar flexors causes a greater amount of hip and knee flexion during the stance phase.
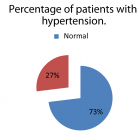
Methodology: 34 subjects with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy who fulfilled all the inclusion criteria were recruited for the study. Ethical standards have been maintained and informed consent was taken. Subjects were randomly assigned by lottery method into two groups, intervention, and control with 17 in each. Since it is a single blinded study subjects were blinded about the interventions provided. Pre and post-test scores were taken before and after 4 weeks using Surface Electromyography (sEMG), Kinovea Software, Functional Gait Assessment (FGA) and Short Form -36 (SF-36).
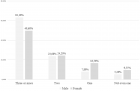
Results: The pre and post-score values of the kinematics of gait, Functional Gait Assessment, and Short Form - 36 were analyzed using a Paired t-test and Wilcoxon Signed Rank test within the group analysis, Mann- Whitney U test and Independent t-test for between the group analysis. Both groups displayed notable variations, whereas the intervention group exhibited more significant differences (p < 0.05). Thus, it can be inferred that lower extremity training significantly improves gait kinematics and quality of life in diabetic neuropathy.
Conclusion: Lower extremity training is effective in improving the kinematics of gait and quality of life in diabetic neuropathy.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001056 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Lower extremity training; Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
References
- Pasnoor M, Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ. Diabetic neuropathy part 2: proximal and asymmetric phenotypes. Neurol Clin. 2013 May;31(2):447-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PMID: 23642718; PMCID: PMC4183450.
- Abdissa D, Hamba N, Kene K, Bedane DA, Etana G, Muleta D, Gerbi A. Prevalence and Determinants of Peripheral Neuropathy among Type 2 Adult Diabetes Patients Attending Jimma University Medical Center, Southwest Ethiopia, 2019, an Institutional-Based Cross-Sectional Study. J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jun 29; 2020:9562920. doi: 10.1155/2020/9562920. PMID: 32685561; PMCID: PMC7341394.
- Andersen H. Motor dysfunction in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012 Feb;28 Suppl 1:89-92. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2257. PMID: 22271730.
- Parasoglou P, Rao S, Slade JM. Declining Skeletal Muscle Function in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Clin Ther. 2017 Jun;39(6):1085-1103. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 30. PMID: 28571613; PMCID: PMC5503477.
- Ernandes RC, Brech GC, Luna NMS, Bega A, GuimarÃes DS, Bocalini DS, Scherrer G, Greve JMD, Leme LEG, Alonso AC. IMPACT OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY ON QUALITY OF LIFE AND POSTURAL BALANCE IN BRAZILIAN OLDER ADULTS. Acta Ortop Bras. 2020 Nov-Dec;28(6):275-279. doi: 10.1590/1413-785220202806234529. PMID: 33328782; PMCID: PMC7723388.
- Ajitha Effectiveness of stability trainer exercises over conventional physiotherapy on balance re-education in patients with type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy. International Journal of Physical Education, Sports and Health. 2020; 7(4):90-97.
- Haregu T, Lekha TR, Jasper S, Kapoor N, Sathish T, Panniyammakal J, Tapp R, Thankappan KR, Mahal A, Absetz P, Fisher EB, Oldenburg B. The long-term effects of Kerala Diabetes Prevention Program on diabetes incidence and cardiometabolic risk: a study protocol. BMC Public Health. 2023 Mar 22;23(1):539. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15392-6. PMID: 36945029; PMCID: PMC10030347.
- Shankar P, Impana G, Kuppusamy S, Jacob R, Sasidharan S: High prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a hospital-based cross-sectional study from South India. 2017. https://morressier.com.
- Hannah J, Sahila Nerve Conduction Study in Children with Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2019; 8(5):289-94.
- Centres for Disease Control and National diabetes statistics report: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States, 2023. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services. 2023.
- Nomura T, Kawae T, Kataoka H, Ikeda Y. Loss of lower extremity muscle strength based on diabetic polyneuropathy in older patients with type 2 diabetes: Multicenter Survey of the Isometric Lower Extremity Strength in Type 2 Diabetes: Phase 2 study. J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Mar;12(3):390-397. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13354. Epub 2020 Aug 12. PMID: 32649788; PMCID: PMC7926230.
- Cimbiz A, Cakir O. Evaluation of balance and physical fitness in diabetic neuropathic patients. J Diabetes Complications. 2005 May-Jun;19(3):160-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2004.06.005. PMID: 15866062.
- Andersen H, Nielsen S, Mogensen CE, Jakobsen J. Muscle strength in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004 Jun;53(6):1543-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.6.1543. PMID: 15161759.
- Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Gait, fifth edition, Joint Structure, and Function: A Compreh 2012; 562-63.
- Henderson AD, Johnson AW, Ridge ST, Egbert JS, Curtis KP, Berry LJ, Bruening DA. Diabetic Gait Is Not Just Slow Gait: Gait Compensations in Diabetic Neuropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2019 Nov 11; 2019:4512501. doi: 10.1155/2019/4512501. PMID: 31815148; PMCID: PMC6878800.
- Alam U, Riley DR, Jugdey RS, Azmi S, Rajbhandari S, D'Août K, Malik RA. Diabetic Neuropathy and Gait: A Review. Diabetes Ther. 2017 Dec;8(6):1253-1264. doi: 10.1007/s13300-017-0295-y. Epub 2017 Sep 1. PMID: 28864841; PMCID: PMC5688977.
- Gomes AA, Ackermann M, Ferreira JP, Orselli MIV, Sacco ICN. Muscle force distribution of the lower limbs during walking in diabetic individuals with and without polyneuropathy. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017 Nov 9;14(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12984-017-0327-x. PMID: 29121964; PMCID: PMC5679149.
- Reeves ND. Gait and Exercise Training in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. The Foot in Diabetes. 2020; 187-200.
- Abadi L, Salahzadeh Z, Rezaei M, Oskouei AE, Azghani MR. Hip joint torques in type II diabetes with and without neuropathy. Hong Kong Physiother J. 2017 Mar 16; 37:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.hkpj.2017.01.004. PMID: 30931043; PMCID: PMC6385154.
- Sylow L, Kleinert M, Richter EA, Jensen TE. Exercise-stimulated glucose uptake - regulation and implications for glycaemic control. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Mar;13(3):133-148. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.162. Epub 2016 Oct 14. PMID: 27739515.
- Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Yardley JE, Riddell MC, Dunstan DW, Dempsey PC, Horton ES, Castorino K, Tate DF. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2016 Nov;39(11):2065-2079. doi: 10.2337/dc16-1728. PMID: 27926890; PMCID: PMC6908414.
- Atre JJ, Ganvir Effect of functional strength training versus proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation on balance and gait in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Indian Journal of Physical Therapy and Research. 2020; 2(1):47.
- Ahmad I, Verma S, Noohu MM, Shareef MY, Hussain ME. Sensorimotor and gait training improves proprioception, nerve function, and muscular activation in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized control trial. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020 Jun 1;20(2):234-248. PMID: 32481239; PMCID: PMC7288382.
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Effect of Lower Extremity Training in Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyAnn Reena Rajan*. Effect of Lower Extremity Training in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001056; 8: 001-004
Recently Viewed
-
Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical PhenotypeDaria A Prokonich*, Tatiana V Saprina, Ekaterina B Bukreeva. Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical Phenotype. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001060; 8: 053-055
-
Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and EmphysemaMJ Nicholson*, M Seigo. Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and Emphysema. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001058; 8: 044-047
-
Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative DisordersShashikant Kharat*, Sanjana Mali*, Gayatri Korade, Rakhi Gaykar. Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001095; 8: 033-046
-
Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of LiteratureNeha Singh,Gaurav Raj,Akshay Kumar,Deepak Kumar Singh,Shivansh Dixit,Kaustubh Gupta*. Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of Literature. J Radiol Oncol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001080; 9: 050-053
-
Validation of Prognostic Scores for Attempted Vaginal Delivery in Scar UterusMouiman Soukaina*,Mourran Oumaima,Etber Amina,Zeraidi Najia,Slaoui Aziz,Baydada Aziz. Validation of Prognostic Scores for Attempted Vaginal Delivery in Scar Uterus. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001185; 8: 023-029
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."